
Electronic Engine Optimization – The Driving Force Behind Engine Management Systems
An engine management system (EMS) is an electronic system that controls various aspects of an internal combustion engine, such as air/fuel mixture, ignition timing, and emissions. It typically includes a computer (engine control unit or ECU) that processes inputs from various sensors and actuators and adjusts different engine parameters accordingly. The EMS aims to optimise engine performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions while ensuring reliable and safe operation.
The EMS controls many critical engine functions and significantly impacts the vehicle’s overall behaviour and efficiency. Modern EMS systems use sophisticated algorithms and control strategies to adjust engine parameters in real time based on various inputs, including throttle position, engine speed, coolant temperature, and exhaust gas oxygen content. They also can diagnose and store fault codes to aid in engine troubleshooting and repair.
Key Engine Management Components and Critical Role That Each Of Them Plays:
An engine management system is the set of components and systems responsible for controlling the operation of an internal combustion engine in a vehicle. The critical engine management components and their essential roles are:
Engine Control Module (ECM):

The central computer monitors and controls all the engine management system components. It receives input from sensors and sends signals to actuators to adjust engine performance and emissions.
Also Read: Equipping Your Workshop – The Must Have Tools for Auto Mechanics
Sensors:
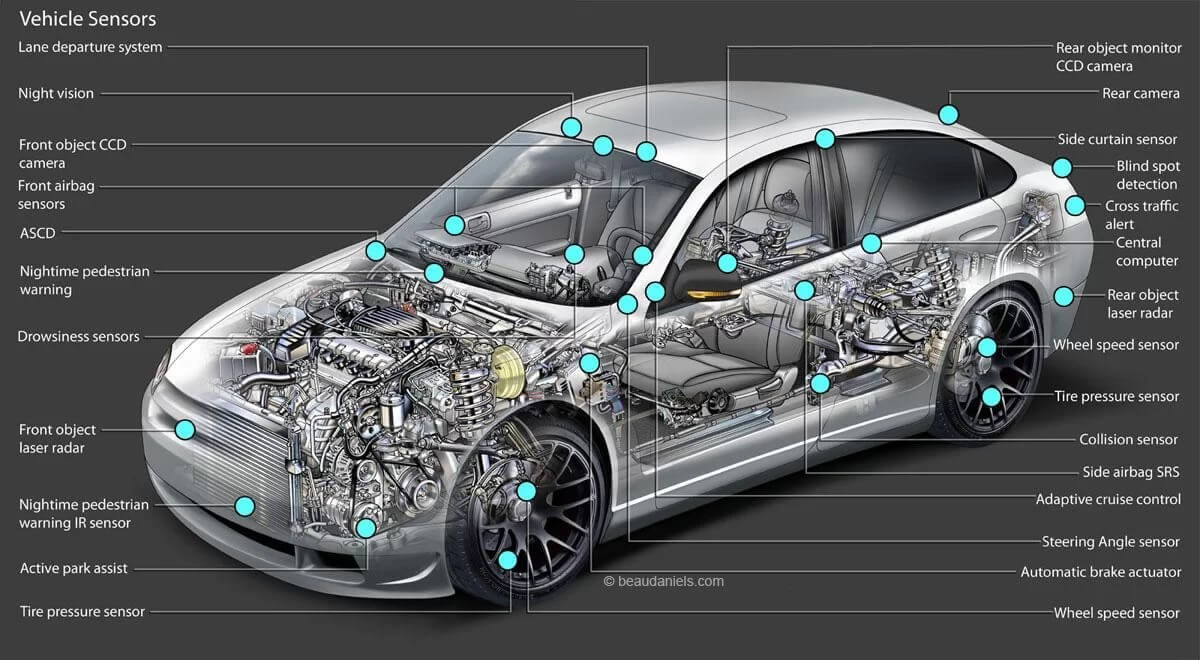
Various sensors in the engine management system provide data to the ECM. Examples include:
- Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor: Measures the amount of air entering the engine.
- Throttle Position Sensor (TPS): Detects the position of the throttle and sends a signal to the ECM to control engine speed.
- Oxygen Sensor (O2 Sensor): Monitors the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gases and provides feedback to the ECM for air/fuel mixture control.
Actuators:

These components perform the ECM’s commands by physically adjusting engine performance. Examples include:
- Fuel Injectors: Fuel injector can control the amount of fuel delivered to the engine.
- Ignition System: Controls the timing and firing of the spark plugs.
- Throttle Body: Adjusts the amount of air entering the engine.
Fuel Delivery System:
The fuel delivery system is responsible for delivering the correct fuel to the engine. It includes the fuel pump, fuel filter, and fuel lines.
These components work together to ensure the engine runs smoothly and efficiently and meets emission standards. They also help to improve fuel economy, performance, and drivability.
Also Read: Everything You Need To Know About Clutch and Its Main Components
What If Engine Management System Malfunctions?
If the Engine Management System (EMS) malfunctions, it can have several consequences for the vehicle, depending on the specific issue. Some common symptoms of an EMS malfunction include:
- Engine misfires or stalls
- Reduced engine power or performance
- Poor fuel economy
- Illumination of the “check engine” light
- Fault codes stored in the EMS system
- Unusual sounds or vibrations from the engine
If the EMS system is not working correctly, it can prevent the engine from functioning at its optimal level, leading to reduced fuel efficiency, decreased performance, and increased emissions. In severe cases, a malfunctioning EMS system can cause damage to the engine and other components of the vehicle.
If you suspect that your vehicle’s EMS system is malfunctioning, it is essential to have it inspected and repaired by a qualified mechanic as soon as possible. Ignoring a problem with the EMS system can lead to further damage and potentially expensive repairs.
Summing It Up:
In conclusion, an Engine Management System (EMS) is a vital component of modern vehicles that controls and manages the engine’s performance. It integrates various sensors and actuators to monitor the engine’s functioning and adjusts multiple parameters such as fuel injection, ignition timing, and valve timing to ensure optimal performance. The EMS also helps reduce emissions and improve fuel efficiency, making it an essential technology for environmental and economic reasons. Additionally, the EMS provides valuable data and diagnostic information that mechanics can use to diagnose and repair issues with the engine. Overall, the Engine Management System plays a critical role in the functioning and performance of modern vehicles, making it an essential technology for the automotive industry.
Image Courtesy: Sensors, Fuel Injectors
